Despite what some may believe, tracking page views and traffic is not necessarily the most important feature of Google Analytics. In fact, this priceless tool can help webmasters and SEOs gain a much deeper, much more relevant understanding of your site’s users.
How can you use Google Analytics to truly drive qualifying traffic towards your website? Below you will find a step-by-step guide to help you set up Goals and make the most of it – so read on and find out more.
Setting Up Goals in Analytics
Although Google Analytics’ “Goals” section is a very complex and useful feature, setting them up is not difficult at all. As long as you know what you want from your website, setting up a Goal to track and sustain your efforts will be quite easy (even for someone who is not an Analytics expert).
- Find the “Goals” in your Google Analytics panel. You should find them in your Google Analytics Standard Reports. Go to the Admin button (top/right side of the screen), click “Goals” and then on “+Goal”. In general, Goals are grouped by sets, so that you can easily organize them according to your particular needs.
- Once you have done this, you will have to name your Goal. Be sure you choose a very specific name you can remember and, more importantly, associate with your campaign’s specific purpose.
- Keep in mind: once added, Goals cannot be deleted. However, they can be activated and de-activated according to what you need.
- There are four main types of Goals you can use in Google Analytics, as follows:
a. Destination URLs
In short, URL goals work well when you want to track specific pages – such as Thank You pages, for example. Basically, what you will have to do here is enter the URL of the page you want Analytics to track. You can use a combination of URL structures by using the drop-down, which includes Equals to, Begins with, and Regular expression. These can be used to combine different pages to one goal (Begins with and Regular expression) or have just one page define the goal (Equals to).
b. Time
This feature is great when you want to track how many people stay on your site for a given amount of time. Furthermore, you can also use this feature to track the people who stay less than a specific amount of time as well.
This is especially useful for customer support pages, when you want to measure how the speed at which your customers find their answers. To track the your support page’s speed, you will have to use the “less than” parameter, while tracking engagement should be used with “greater than”.
c. Page/Visits
Tracking the number of pages your visitors see on each visit is important as well – especially for customer support pages. Similarly to duration tracking, the “greater than” parameter will help you measure engagement and “less than” will measure the effectiveness of your customer support.
d. Events
Probably the most complex type of Goal you can set up in Analytics, Events are an excellent way to track the performance of a variety of special features on your website. Some of them include downloads, the time customers spend on your videos, how your widgets are used, and so on.
The reason this particular type of Goal is more complicated than the others is because you will have to add a bit of JavaScript to the element. Fortunately though, Google has put up an entire tutorial on how you can do this. If you do not have any kind of coding knowledge, this might need the help of a developer. You can also add these through Google Tag Manager, but this might require a developer as well.
When you set up Event Goals, it is extremely important to remember that they are defined by a category, an action, a label and a value. If you only set up one of them, Google Analytics will not consider the other ones in the report. If you use all of them, events will be recorded only if all four criteria are met. Therefore, it is crucial that you give these some thinking before jumping to action.
Sales Funnels and Goals
Goals can become an integral part of your Conversions Funnel. This will help you track your users and see exactly when each one of them leaves the sales process, why they are doing this and, more importantly, what you can do to make sure they either don’t leave in the first place or they return as leads.
Google Analytics will only allow you to introduce 10 steps as part of the Funnel. Moreover, it is extremely important that you use this only when your users’ path is very clear. If, in general, your users follow a more unstructured path on your website (the vast majority of the cases), you can use the Users Flow feature in Google Analytics – Funnels will not work in this case.
Same as with URLs, it is also essential that you match type the name of the steps with the corresponding page name. Although Analytics will track your users’ movement through the Funnel even if they jump in right in the middle, it will not track them if the page names and steps are not properly coordinated.
Reverse Goal Path is another type of report available in Google Analytics which can be helpful when analyzing irregular customer paths. You will find this one in the left side of Google Analytics, under Conversions -> Goals. This will allow you to select a particular Goal you have already set, so that you can see what pages users come from when they reach that Goal. The report goes as far back as 3 pages, meaning that it can be used for unstructured user paths as well.
Pro Tip
Since Google Analytics will only allow you to introduce 10 steps as part of the Funnel, it is extremely important that you use this only when your users’ path is very clear.
Can You Track Conversion Keywords?
Until not very long ago, Google Analytics provided webmasters with the exact search queries that landed users on their websites. However, as of recently, they have stopped doing this – leaving SEOs and webmasters guessing for the keywords that work and don’t work on their specific campaigns.
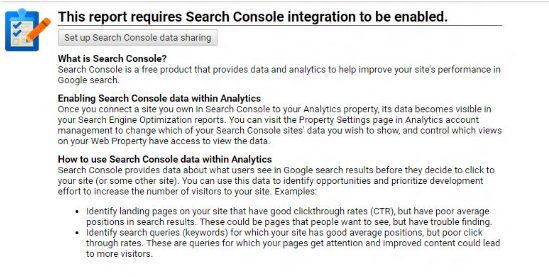
However, tracking the search queries that bring people on your website can be done. Make sure you have verified your site in Google Search Console, then follow these steps:
- Go to Acquisition > Search Console > Queries
- Click on Setup Search Console Data Sharing:
- Scroll down to Adjust Search Console and click on the button;
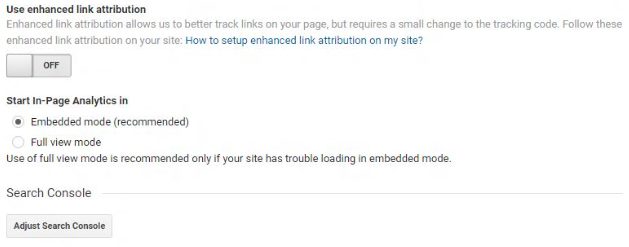
4. Select the Google Webmasters account that corresponds to your Google Analytics profile.
5. This will enable three new reports in your main page: Queries, Landing Page and Geographical Summary.
6. The Queries report will show you what keywords users search for to reach your site, how many impressions they get, where they rank in Google, and so on. The same report will also show you the click-through-rate as well – and this is an extremely important metric to follow if you want to improve your SEO performance.
At the end of the day, Google Analytics is an indispensable tool for anyone who wants to be genuinely present in the digital world. Learn how to work with its reports and Goals, and make sure you make the most of it all – it can definitely help you boost your site and your campaigns’ efficiency.

